Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- 백트래킹
- 카프카
- gcp
- 스프링부트
- Spring
- Kafka
- Docker
- 로드밸런서
- Spring Data JPA
- 프로그래밍문제
- DFS
- 클라우드
- aws
- 스프링
- VPC
- 스프링 부트
- 쿠버네티스
- Spring Boot
- springboot
- 클라우드 컴퓨팅
- 개발
- JPA
- 오일러프로젝트
- 알고리즘
- 자료구조
- 코드업
- 머신러닝
- Elasticsearch
- 백준
- Apache Kafka
Archives
- Today
- Total
GW LABS
C++로 구현하는 자료구조 (6) - Stack 본문

C++로 구현하는 자료구조 6번째 포스팅이다. 스택은 앞서 구현한 동적배열, 연결리스트를 이용하면 간결하게 구현할 수 있다. 동작원리는 간단하나, 알고리즘 문제들에서는 스택을 사용해서 해결해야겠다는 아이디어를 떠올리기가 어렵다. 이번 포스팅에서 스택을 이해하고 활용할 수 있도록 노력해보자.
1. Stack
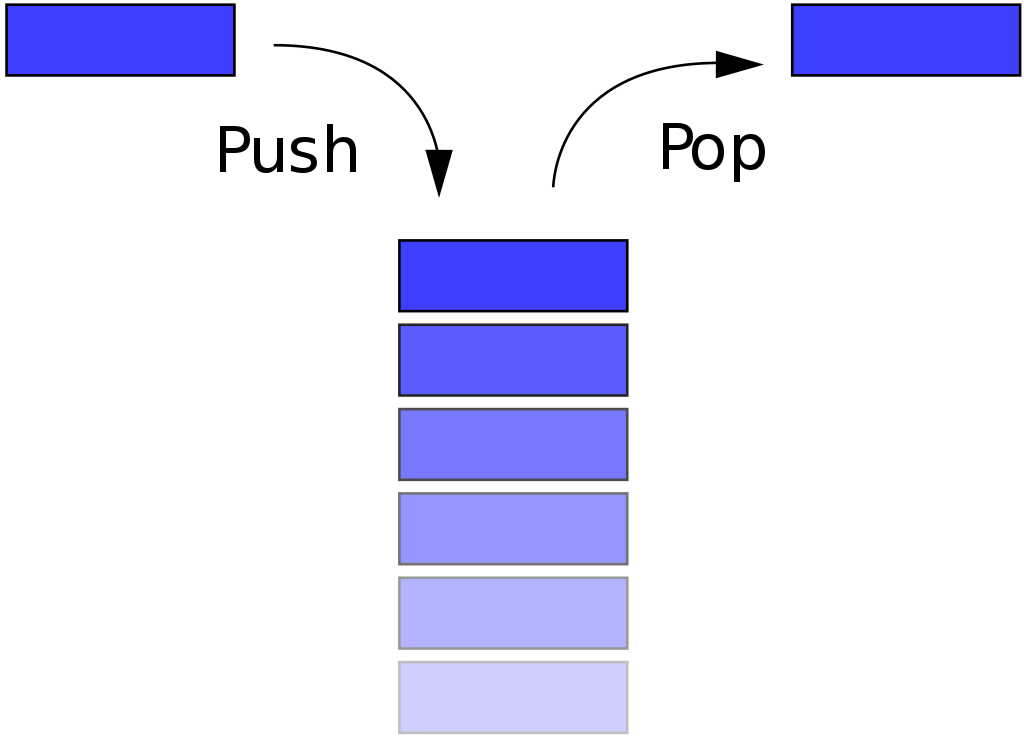
스택은 First in, Last out 형태의 선형 자료구조이다. 스택의 경우 구현은 쉬운 편이다. 앞서 구현한 연결리스트 혹은 동적배열 등을 이용해서 구현이 가능하다. 연결리스트를 이용해 구현할 때에는 맨 뒤의 노드에 추가, 삭제만 해주는 형식으로 구현하면 된다. 동적배열의 경우에도 가장 뒤의 요소에 추가, 삭제하는 형식으로 접근하면 손쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
2. Stack의 기능들
스택 자료구조를 지원하는 대부분의 언어들은 공통적으로 다음과 같은 연산들을 지원하고 있다.
-
top : 스택의 가장 위의 데이터를 가져온다.
-
push : 스택에 데이터를 추가한다.
-
pop : 스택에 데이터를 제거한다.
-
empty : 스택에 데이터가 비어있는지 확인한다.
3. 소스코드
이번 포스팅에서는 스택을 동적배열을 이용해서 구현했다.
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
template <typename T>
class Stack {
private:
int size;
T* container;
int sizeContainer;
// 스택 컨테이너의 사이즈를 재조정한다.
void resizeContainer() {
this->sizeContainer *= 2;
T* tmpContainer = new T[this->sizeContainer];
for (int idx = 0; idx < this->size; idx++) {
tmpContainer[idx] = this->container[idx];
}
delete[] this->container;
this->container = tmpContainer;
}
public:
Stack() {
this->size = 0;
this->sizeContainer = 2;
this->container = new T[this->sizeContainer];
}
void push(T element) {
if (this->sizeContainer == this->size) {
this->resizeContainer();
}
this->size++;
this->container[this->size - 1] = element;
}
bool empty() {
if (this->size == 0) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
void pop() {
if (this->empty()) {
std::cout << "스택에 원소가 없습니다." << std::endl;
}
else {
this->size--;
}
}
T top() {
return this->container[this->size - 1];
}
~Stack() {
delete[] this->container;
}
};#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "datastructure/Stack.h"
int main() {
Stack<std::string>* stack = new Stack<std::string>();
stack->pop();
stack->push("1");
stack->push("2");
stack->push("3");
std::cout << stack->top() << std::endl;
stack->pop();
std::cout << stack->top() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
'Algorithm & DataStructure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Backjoon] 토마토 (0) | 2020.10.17 |
|---|---|
| C++로 구현하는 자료구조 (7) - Queue (0) | 2020.10.13 |
| [Backjoon] 뱀 (0) | 2020.10.06 |
| [Backjoon] 프린터 큐 (0) | 2020.10.04 |
| [Backjoon] 안전영역 (0) | 2020.09.30 |
Comments

